One of the most important issues in energy conservation areas and solar energy use is undoubtedly homes and workplaces air conditioning application.
This sector accounts about 40% of the total energy consumed. The savings can be achieved by using solar energy for heating is of the order of 60% to 80% depending on house design.
The principles of bioclimatic architecture should be applied in all new urban plans.
When speaking of passive solar architecture, we talk about modeling, selection and use of passive solar technology, which is capable of maintaining a comfortable and pleasant temperature home environment through the sun. This type of architecture is only a small part of the energy efficient buildings design and is considered as part of sustainable design.
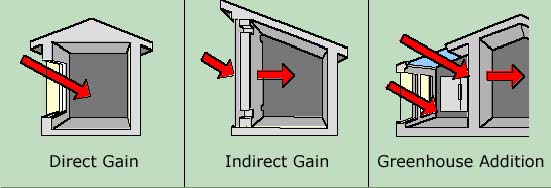
There are three types of solar gain:
1) Direct solar gain: refers to the use of windows, skylights and blinds to control the amount of solar radiation reaching the inside of a housing, in combination with mass floors.
2) Indirect solar gain: is achieved through the skin of the building, designed with certain thermal mass. An example of this gain is also the garden roof.
3) Isolated solar gain: is the process in which the main thing is the sun heat passive capture, and then transport it inside or outside the home.
There are considerations to take into account in this type of architecture implementation, to give his best result:
* Building orientation
* Construction features
* Environment use

In existing buildings we can always intervene to improve thermal insulation, sun blinds open in winter or adding a glass gallery on the north side of the house if we are located in the southern hemisphere.
To heat the house with the sun, a clear winter north facade without many neighbors who clog the midday sun is needed.
Main glazings must be on the north facade. For example, if we are located in the southern half of Argentina we need 1.4 to 2 m2 of north glass for every 10 m2 stay we want to heat.
Windows should be closed with curtains or blinds at night to heat captured not escape. It is good to improve thermal insulation as far as possible and have thermal mass (building material in walls, floors) which accumulate the heat of the day to the night. For summer it is necessary to place eaves, awnings, vines, etc. that shade windows in.
You can acces more Spanish language content like this in Manual Técnico – Comercial de Energía Solar Térmica by Sopelia.